How Products Are Developed
How Products Are Developed
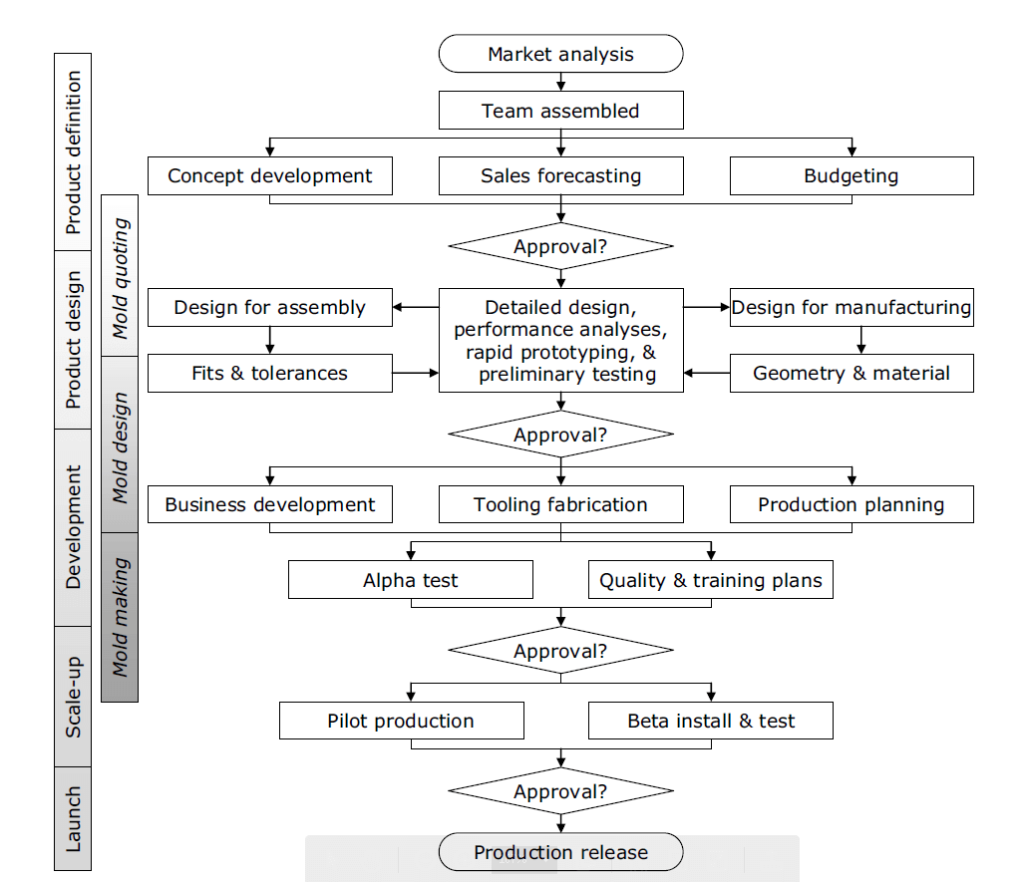
A key component of product development is mold design. The relationship between product and mold design is such that both product and mold design engineers will benefit from knowledge of the design and production of plastics parts and molds. In Figure below you will see the steps involved in the typical product development process, which includes concept development, product design, business planning, and launch.
While the process itself varies, the two characteristics that are common to most are:
- In order to ensure the design and manufacturing process are complete and on track, a development plan is necessary.
- Using the toll-gate method, a larger budget is approved only after significant reviews are conducted towards project progress.
Fig. 2.1 shows the stages of product development separated by the approval tollgates. Following is a description of each stage.
-
Determination of the product
Analyzing the market, benchmarking competitors, defining product specifications, and assessing profitability are common elements of the product development process. An early business concept can be developed only if the company's management decides a new product should be developed. In this first stage, the size, properties, and cost of the product are estimated. For communication and assessment, prototypes, mockups, and sketches can be produced.
Early product development market studies will attempt to predict the potential sales at different price points with regard to profitability. In addition, manpower and project cost estimates will determine the budget needed for the development and marketing of the product. To assess whether the continued development of a product will be commercially successful, management reviews the concept design, sales forecast, and budget. The proposed product development project may be declined, shelved, or modified at this time.
-
The Design of a Product
Once a product development project has been approved and a budget allocated, it is usually followed by additional resources to carry out further analysis and design. A detailed design is completed for each component in this second stage. Plastic components are designed according to a variety of factors, such as aesthetics, structural, thermal, manufacturing, and others. It might be useful to use design for manufacturing methods to identify issues that might prevent the components from being manufactured effectively. Assembly design methods can be used to reduce component numbers, specify critical dimensions with tolerances, and ensure that finished products can be assembled economically.
At the end of the first product design stage, a fully developed and proven design is ready. As a result of "detailed design," every component is completely specified in terms of material, geometric form, surface finish, tolerances, cost, and supplier. Often, during this stage, molded parts quotes will be requested if the project calls for a custom plastic component. The quotes and the detailed design are then submitted to management for approval. In the manufacturing phase, a budget is allocated after the product design and costs have been approved.
-
Develop sales and productivity
Figure 2.1 shows that plastics industry professionals concentrate on designing and making molds, but that these activities are included within the “Tooling Fabrication” activity. At the same time, business development and production planning are also important activities. This includes establishing initial orders to support the launch of the product as well as defining the supply chain. Assembly lines require planning, as do labor requirements and the production system.
Following the tooling completion, the "alpha" parts are manufactured, tested, and assembled. In the end, the alpha product is put through a series of tests to ensure compliance, performance, and user satisfaction. Modifications to the manufacturing process, tooling, and detailed component designs are made, if necessary, in response to the assembled alpha product not being satisfactory. A detailed plan is also developed for quality control and worker training by those in charge of operations.
-
Growing your business and launching it
Management often reviews products and production plans to ensure they meet its standards. So, a small quantity of products can be manufactured in a pilot production run according to the standard manufacturing conditions. Marketers, sales people, and key customers often test "Beta" products once they are manufactured. In the same way, any significant issues will be addressed through a redesign and remanufacturing of the product. An initial inventory of the product is built during the pilot production process, and then the product can be released for sale. When all the participants ( promotion, manufacturing, vendors, and critical customers) are ready, this process is completed.
-
Mold design plays an important role
Quoting, design, and manufacture of molds are all a part of the larger product development process. A request for price quotes on molds and/or parts is typically submitted near the end of conceptual design or shortly after detailed design begins. Mold design details are generally not provided when the product is under development, as 1) much of the mold design work could have been done concurrently with a less developed product design and 2) the mold engineering process may suggest changes to the design that will enhance the part's machineability or performance.
It's not uncommon for molds to be designed in the early stages of development that lack detail and would produce an unsatisfactory result if implemented directly. For the purpose of designing a mold, the critical design information of the part must be obtained, such as its size, wall thickness, and expected production quantity. Mold designers use this information to develop initial mold layouts, estimate costs, and improve design concepts. Mold development can be accelerated by purchasing and customizing mold components simultaneously with mold design.
Whether for good or for bad, the final step in product development is making and commissioning molds. As a consequence, mold manufacturers and suppliers may feel considerable pressure to provide quality molds as quickly as possible. This task can be extremely challenging as a result of potentially costly mistakes made earlier in the process. For this reason, certain parts of the mold may need to be redesigned and changed if the mold is to be qualified for production.
https://www.plasticmoulds.net/how-products-are-developed.html
A key component of product development is mold design. The relationship between product and mold design is such that both product and mold design engineers will benefit from knowledge of the design and production of plastics parts and molds. In Figure below you will see the steps involved in the typical product development process, which includes concept development, product design, business planning, and launch.

While the process itself varies, the two characteristics that are common to most are:
- In order to ensure the design and manufacturing process are complete and on track, a development plan is necessary.
- Using the toll-gate method, a larger budget is approved only after significant reviews are conducted towards project progress.
Fig. 2.1 shows the stages of product development separated by the approval tollgates. Following is a description of each stage.
-
Determination of the product
Analyzing the market, benchmarking competitors, defining product specifications, and assessing profitability are common elements of the product development process. An early business concept can be developed only if the company's management decides a new product should be developed. In this first stage, the size, properties, and cost of the product are estimated. For communication and assessment, prototypes, mockups, and sketches can be produced.
Early product development market studies will attempt to predict the potential sales at different price points with regard to profitability. In addition, manpower and project cost estimates will determine the budget needed for the development and marketing of the product. To assess whether the continued development of a product will be commercially successful, management reviews the concept design, sales forecast, and budget. The proposed product development project may be declined, shelved, or modified at this time.
-
The Design of a Product
Once a product development project has been approved and a budget allocated, it is usually followed by additional resources to carry out further analysis and design. A detailed design is completed for each component in this second stage. Plastic components are designed according to a variety of factors, such as aesthetics, structural, thermal, manufacturing, and others. It might be useful to use design for manufacturing methods to identify issues that might prevent the components from being manufactured effectively. Assembly design methods can be used to reduce component numbers, specify critical dimensions with tolerances, and ensure that finished products can be assembled economically.
At the end of the first product design stage, a fully developed and proven design is ready. As a result of "detailed design," every component is completely specified in terms of material, geometric form, surface finish, tolerances, cost, and supplier. Often, during this stage, molded parts quotes will be requested if the project calls for a custom plastic component. The quotes and the detailed design are then submitted to management for approval. In the manufacturing phase, a budget is allocated after the product design and costs have been approved.
-
Develop sales and productivity
Figure 2.1 shows that plastics industry professionals concentrate on designing and making molds, but that these activities are included within the “Tooling Fabrication” activity. At the same time, business development and production planning are also important activities. This includes establishing initial orders to support the launch of the product as well as defining the supply chain. Assembly lines require planning, as do labor requirements and the production system.
Following the tooling completion, the "alpha" parts are manufactured, tested, and assembled. In the end, the alpha product is put through a series of tests to ensure compliance, performance, and user satisfaction. Modifications to the manufacturing process, tooling, and detailed component designs are made, if necessary, in response to the assembled alpha product not being satisfactory. A detailed plan is also developed for quality control and worker training by those in charge of operations.
-
Growing your business and launching it
Management often reviews products and production plans to ensure they meet its standards. So, a small quantity of products can be manufactured in a pilot production run according to the standard manufacturing conditions. Marketers, sales people, and key customers often test "Beta" products once they are manufactured. In the same way, any significant issues will be addressed through a redesign and remanufacturing of the product. An initial inventory of the product is built during the pilot production process, and then the product can be released for sale. When all the participants ( promotion, manufacturing, vendors, and critical customers) are ready, this process is completed.
-
Mold design plays an important role

Quoting, design, and manufacture of molds are all a part of the larger product development process. A request for price quotes on molds and/or parts is typically submitted near the end of conceptual design or shortly after detailed design begins. Mold design details are generally not provided when the product is under development, as 1) much of the mold design work could have been done concurrently with a less developed product design and 2) the mold engineering process may suggest changes to the design that will enhance the part's machineability or performance.
It's not uncommon for molds to be designed in the early stages of development that lack detail and would produce an unsatisfactory result if implemented directly. For the purpose of designing a mold, the critical design information of the part must be obtained, such as its size, wall thickness, and expected production quantity. Mold designers use this information to develop initial mold layouts, estimate costs, and improve design concepts. Mold development can be accelerated by purchasing and customizing mold components simultaneously with mold design.
Whether for good or for bad, the final step in product development is making and commissioning molds. As a consequence, mold manufacturers and suppliers may feel considerable pressure to provide quality molds as quickly as possible. This task can be extremely challenging as a result of potentially costly mistakes made earlier in the process. For this reason, certain parts of the mold may need to be redesigned and changed if the mold is to be qualified for production.
https://www.plasticmoulds.net/how-products-are-developed.html
Comments
Post a Comment