temperature control of injection mold
The temperature of the injection mold has a great influence on the filling, solidification , production efficiency, and the shape and dimensional accuracy of the plastic parts.
Each kind of plastic material has a reasonable mold temperature arrange, which makes the melt flow easily fill the cavity.
If the mold temperature is reasonable, the shrinkage and warping deformation of the plastic parts after demoulding will be small, the size will be stable, and the mechanical properties and surface quality will also be good.
In order to control the temperature of the mold, a temperature adjusting system must be designed.
Generally, the mold should be cooled or heated. If necessary, there are both needed.
In plastic injection molding, the temperature of the melt in the cavity is generally between 200 and 300 degree, the melt is formed in the cavity, cooled, and solidified into a product profile.

When the injection molded product is taken out of the mold, the temperature is generally 60 degree about, the heat released by the melt is transferred to the mold.
In order to ensure smooth production, the mold must pass the heat out in time, so that the temperature is always controlled within a reasonable range. The structure that carry the heat out is called the cooling system.
The heat transfer is conducted by conduction, convection and radiation, and 95% of the heat in the mold is carried away by heat conduction.
The medium for heat conduction in the mold is mainly cooling water (including normal temperature water and frozen water), and sometimes oil and beryllium copper.
The convective heat transfer in the mold is mainly carried out by means of a fan, and the mold is naturally cooled in the air.
The injection mold is firstly a production tool, which can repeatedly and mass-produce plastic products with the same structure and the dimensional accuracy.
Secondly, it is a heat exchanger. In order to ensure the molding quality and production efficiency, it is necessary to use the medium to heat or cool the mold until temperature reaches within a reasonable range.
The section of the mold that continuously transfers heat from the melt or heats the mold to the normal injection temperature is called a temperature control system.
Mold temperature refers to the surface temperature of the mold cavity that is in contact with the molded part, it directly affects the flow of the melt, the cooling of the mold, and the quality of the product.
The productivity of the mold depends on the speed of heat exchange. The mold heat exchange depends on the temperature of the melt, the molded parts release temperature and the enthalpy of the plastic.
For molds with high precision and mass production demands, the design of the temperature control system is very strict. Sometimes a special temperature regulator must be designed to strictly control the temperature of each part of the mold.
The temperature control system of this type of injection mold is one of the difficulties in mold design.
The mold temperature control system includes 2 systems: cooling or heating the mold.
However, for plastics with poor viscosity and poor fluidity, such as PC, hard PVC, PSF, PPO, etc., the mold temperature can better improve the fluidity.
The mold temperature should be controlled between 80 and 120 °C.
For these molds, if the surface dissipates heat quickly, the heat of the melt alone is not enough to maintain the mold temperature.
Therefore, the mold needs to be equipped with a heating system to heat.
[table id=5 /]
Some molds have both a cooling system and a heating system.
Production in cold area or for a large mold, the mold must be preheated before the mold run smoothly.
When the temperature of the mold reaches the molding demand, the heating system can be turned off.
If the temperature of the mold is higher after a period of time production.
When the molding temperature is required, the cooling system of the mold is adopted again.
if the plastic product is large and its wall thickness is uneven, it is need be cooled at the thick wall section and heated at the thin wall section to improve the melt flow.
For small thin-walled products, the molding process requires not low mold temperature, a heating device or a cooling device may not be provided, and the mold is cooled naturally.
In injection molding, the temperature of the mold directly affects the filling, solidifying, the quality, and the cycle of the mold.
For plastics with good fluidity such as PE, PP, HIPS, ABS, etc., reducing the mold temperature can reduce stress cracking, and the mold temperature should be controlled at 60 degree about, a cooling system must be provided for this mold.
For plastics with poor fluidity such as PC, PPO, PSF, etc., increasing the mold temperature is beneficial to reduce the internal stress of the product.
The mold temperature should be controlled between 80 and 120 °C. For this purpose, a heating system should be installed.
In addition, the cooling process of crystalline plastics (such as PE, PP, POM, PA, PET, etc.) and amorphous plastics (such as PS, HIPS, PVC, PMMA, PC, ABS, polysulfide, etc.) are different.
For crystalline plastics, when cooling through the crystallization zone, the heat is released, but the temperature of the plastic remains the same.
Only after the crystallization zone, the plastic can be further cooled. Therefore, the crystalline plastic needs take more heat away when the cooling, compared to that of the amorphous plastic.
Table below lists the plastic barrel temperature and mold temperature commonly used when there is no special requirement for the surface quality of the product (ie, the general surface) (the mold temperature in the table is the temperature of the mold cavity).
If the mold temperature is too high, the molding shrinkage will be uneven, and the product is deformed greatly after demolding.it is easy to cause flash and sticking to cavity and core.
If the mold temperature is too low, the melt fluidity is poor, and the surface may have obvious defects such as silver streaks or flow marks.
When the temperature of the mold is not uniform, the temperature of the molded product, after solidifying in the mold cavity, is not uniform, it will result in uneven shrinkage, internal stress, deformation, cracking, and warpage of the product after the product is released from the mold.
Therefore, the all parts of the product must be balance cooled.
The fluctuation of the mold temperature has a great influence on the shrinkage rate, dimensional stability, deformation, stress cracking, and surface quality.
The cooling time is approximately 80% about the molding cycle.
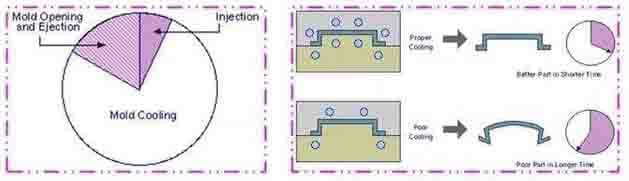
If the mold temperature is well controlled, the melt can be solidified in time. mold is opened and the molded product is taken out in a shorter time, the molding cycle will be shortened, but if the mold temperature is not well controlled, the melt is solidified slowly, which not only fails to lower the mold temperature, but the most seriously, it even had to stop and rest to cool the mold, which resulted in a longer mold injection cycle and reduced productivity.
[divider_line]
(1) The number of cooling channels should be as many as possible and the channels diameter should be as large as possible.
The distance between the center line of the cooling channels and the mold wall should be 1-2 times (usually 12 mm~15 mm) of the diameter of the cooling water channel, and the center distance between the cooling water channels should be about 3-5 times of the diameter of the water channels.
Channels diameter is generally above 8 mm.
(2) The distance between the cooling channels and the mold surface should be as equal as possible.
When the wall thickness of the plastic part is uniform, the distance between the cooling water hole and the surface of the cavity should be equal everywhere as far as possible.
But,if the wall thickness of the plastic part is uneven, the cooling should be strengthened at the thick wall.
(3) Gate cooling should be strengthened.
(4) cooling channel should not pass through the insert or its joint parts to prevent water leakage.
(5) Cooling channel location should be avoided at weld lines of plastic parts.
(6) The position of the inlet and outlet water pipe joints shall be located on the same side of the mold as far as possible, usually on the other side of the operator side.
Each kind of plastic material has a reasonable mold temperature arrange, which makes the melt flow easily fill the cavity.
If the mold temperature is reasonable, the shrinkage and warping deformation of the plastic parts after demoulding will be small, the size will be stable, and the mechanical properties and surface quality will also be good.
In order to control the temperature of the mold, a temperature adjusting system must be designed.
Generally, the mold should be cooled or heated. If necessary, there are both needed.
In plastic injection molding, the temperature of the melt in the cavity is generally between 200 and 300 degree, the melt is formed in the cavity, cooled, and solidified into a product profile.

When the injection molded product is taken out of the mold, the temperature is generally 60 degree about, the heat released by the melt is transferred to the mold.
In order to ensure smooth production, the mold must pass the heat out in time, so that the temperature is always controlled within a reasonable range. The structure that carry the heat out is called the cooling system.
The heat transfer is conducted by conduction, convection and radiation, and 95% of the heat in the mold is carried away by heat conduction.
The medium for heat conduction in the mold is mainly cooling water (including normal temperature water and frozen water), and sometimes oil and beryllium copper.
The convective heat transfer in the mold is mainly carried out by means of a fan, and the mold is naturally cooled in the air.
The injection mold is firstly a production tool, which can repeatedly and mass-produce plastic products with the same structure and the dimensional accuracy.
Secondly, it is a heat exchanger. In order to ensure the molding quality and production efficiency, it is necessary to use the medium to heat or cool the mold until temperature reaches within a reasonable range.
The section of the mold that continuously transfers heat from the melt or heats the mold to the normal injection temperature is called a temperature control system.
Mold temperature refers to the surface temperature of the mold cavity that is in contact with the molded part, it directly affects the flow of the melt, the cooling of the mold, and the quality of the product.
The productivity of the mold depends on the speed of heat exchange. The mold heat exchange depends on the temperature of the melt, the molded parts release temperature and the enthalpy of the plastic.
For molds with high precision and mass production demands, the design of the temperature control system is very strict. Sometimes a special temperature regulator must be designed to strictly control the temperature of each part of the mold.
The temperature control system of this type of injection mold is one of the difficulties in mold design.
The mold temperature control system includes 2 systems: cooling or heating the mold.
However, for plastics with poor viscosity and poor fluidity, such as PC, hard PVC, PSF, PPO, etc., the mold temperature can better improve the fluidity.
The mold temperature should be controlled between 80 and 120 °C.
For these molds, if the surface dissipates heat quickly, the heat of the melt alone is not enough to maintain the mold temperature.
Therefore, the mold needs to be equipped with a heating system to heat.
[table id=5 /]
Some molds have both a cooling system and a heating system.
Production in cold area or for a large mold, the mold must be preheated before the mold run smoothly.
When the temperature of the mold reaches the molding demand, the heating system can be turned off.
If the temperature of the mold is higher after a period of time production.
When the molding temperature is required, the cooling system of the mold is adopted again.
if the plastic product is large and its wall thickness is uneven, it is need be cooled at the thick wall section and heated at the thin wall section to improve the melt flow.
For small thin-walled products, the molding process requires not low mold temperature, a heating device or a cooling device may not be provided, and the mold is cooled naturally.
- Importance of temperature control
In injection molding, the temperature of the mold directly affects the filling, solidifying, the quality, and the cycle of the mold.
For plastics with good fluidity such as PE, PP, HIPS, ABS, etc., reducing the mold temperature can reduce stress cracking, and the mold temperature should be controlled at 60 degree about, a cooling system must be provided for this mold.
For plastics with poor fluidity such as PC, PPO, PSF, etc., increasing the mold temperature is beneficial to reduce the internal stress of the product.
The mold temperature should be controlled between 80 and 120 °C. For this purpose, a heating system should be installed.
In addition, the cooling process of crystalline plastics (such as PE, PP, POM, PA, PET, etc.) and amorphous plastics (such as PS, HIPS, PVC, PMMA, PC, ABS, polysulfide, etc.) are different.
For crystalline plastics, when cooling through the crystallization zone, the heat is released, but the temperature of the plastic remains the same.
Only after the crystallization zone, the plastic can be further cooled. Therefore, the crystalline plastic needs take more heat away when the cooling, compared to that of the amorphous plastic.
Table below lists the plastic barrel temperature and mold temperature commonly used when there is no special requirement for the surface quality of the product (ie, the general surface) (the mold temperature in the table is the temperature of the mold cavity).
- Effect on product accuracy
If the mold temperature is too high, the molding shrinkage will be uneven, and the product is deformed greatly after demolding.it is easy to cause flash and sticking to cavity and core.
If the mold temperature is too low, the melt fluidity is poor, and the surface may have obvious defects such as silver streaks or flow marks.
When the temperature of the mold is not uniform, the temperature of the molded product, after solidifying in the mold cavity, is not uniform, it will result in uneven shrinkage, internal stress, deformation, cracking, and warpage of the product after the product is released from the mold.
Therefore, the all parts of the product must be balance cooled.
The fluctuation of the mold temperature has a great influence on the shrinkage rate, dimensional stability, deformation, stress cracking, and surface quality.
- Effect on injection molding cycle
The cooling time is approximately 80% about the molding cycle.
If the mold temperature is well controlled, the melt can be solidified in time. mold is opened and the molded product is taken out in a shorter time, the molding cycle will be shortened, but if the mold temperature is not well controlled, the melt is solidified slowly, which not only fails to lower the mold temperature, but the most seriously, it even had to stop and rest to cool the mold, which resulted in a longer mold injection cycle and reduced productivity.
[divider_line]
Design Principles of Cooling channels

(1) The number of cooling channels should be as many as possible and the channels diameter should be as large as possible.
The distance between the center line of the cooling channels and the mold wall should be 1-2 times (usually 12 mm~15 mm) of the diameter of the cooling water channel, and the center distance between the cooling water channels should be about 3-5 times of the diameter of the water channels.
Channels diameter is generally above 8 mm.
(2) The distance between the cooling channels and the mold surface should be as equal as possible.
When the wall thickness of the plastic part is uniform, the distance between the cooling water hole and the surface of the cavity should be equal everywhere as far as possible.
But,if the wall thickness of the plastic part is uneven, the cooling should be strengthened at the thick wall.
(3) Gate cooling should be strengthened.
(4) cooling channel should not pass through the insert or its joint parts to prevent water leakage.
(5) Cooling channel location should be avoided at weld lines of plastic parts.
(6) The position of the inlet and outlet water pipe joints shall be located on the same side of the mold as far as possible, usually on the other side of the operator side.
Comments
Post a Comment